Volatility in forex trading
The world of Forex often feels like riding the waves of a vast ocean. Some days are calm, while others witness tempestuous tides. It’s this unpredictable movement we term “volatility’ in forex trading. What is important is learning how to manage the risks involved in the unpredictable volatile world of forex, taking into consideration the trader’s risk tolerance. So, let’s delve deep into the sea of market volatility in forex trading.
What is Volatility in forex trading?
Just Imagine- You throw a stone into a serene pond. The impact causes ripples, disrupting the calm. Similarly, in the trading realm, Volatility is the degree of variation of a trading price series over time. It gauges the difference between highs and lows and ultimately, the risk and uncertainty of returns.
Why is Volatility in forex trading important?
Volatility in forex trading is like the spices in a dish. High volatility may offer trading potential, but it also comes with greater risks. Conversely, low volatility may indicate a more stable environment but may offer fewer opportunities.
What are the most volatile markets?
If the forex market were a zoo, then the most volatile currency pairs would be the wild animals you’re both excited and cautious to observe. Pairs like GBP/JPY, EUR/NZD, and AUD/JPY have earned their reputation due to significant price fluctuations. Trading volatility becomes more evident in these pairs, making them both a potential opportunity and a challenge for traders.
Volatility Trading Strategies
Like surfers have their tricks to ride the waves, traders can have their own volatility trading strategies. Here are a few examples of approach:
- Straddle Strategy: Involves buying a call and putting an option with identical strike prices and expiry dates. It’s a speculation movement without pinpointing a direction.
- Delta Hedging: This involves offsetting a position in the underlying asset with a corresponding option position.
- Long Volatility: Involves buying options when expecting a significant market move, hoping to get potential gains from potential increased volatility.
What causes market volatility of Currency Pairs?
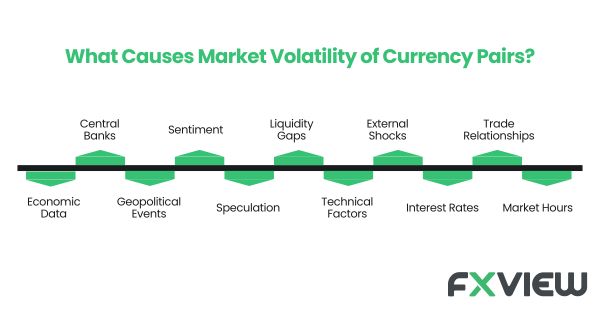
Several elements stir the pot of market volatility in forex trading. Key drivers include:
- Economic Data: Economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment figures, inflation rates, and central bank interest rate decisions can trigger rapid and unpredictable price movements in currency pairs.
- Central Banks: Decisions and statements from central banks, especially those regarding interest rates and monetary policy, may wield significant influence over currency values, causing potential fluctuations when markets react to these announcements.
- Geopolitical Events: Political instability, elections, trade disputes, and geopolitical conflicts may introduce uncertainty and drive market volatility as traders respond to unforeseen developments.
- Sentiment: Market sentiment, shaped by traders’ perceptions of economic and political conditions and their risk appetite, can lead to abrupt shifts in currency pair values.
- Speculation: Traders, including institutional investors and speculators, can instigate volatility through their trading activities, especially when managing large positions, dealing with stop-loss orders, or facing margin calls that prompt swift price movements.
- Liquidity Gaps: Periods of low liquidity, such as market openings or major holidays, can lead to erratic price fluctuations as even a few trades can significantly impact prices.
- Technical Factors: Technical analysis, including the use of support and resistance levels, moving averages, and chart patterns, can trigger increased trading activity and associated volatility when these technical levels are breached.
- External Shocks: Unexpected events unrelated to financial markets, like natural disasters, terrorist attacks, or health crises such as the COVID-19 pandemic, can result in heightened market volatility as traders adjust to new realities and assess potential economic consequences.
- Interest Rates: Differences in interest rates between two countries can influence currency pair volatility, with higher interest rates relative to another country attracting capital inflows, leading to currency appreciation, and rate cuts or expectations of rate cuts potentially causing depreciation.
- Trade Relationships: Economic and trade connections between countries may significantly impact currency pair movements; trade surpluses or deficits, tariffs, and trade agreements can all lead to volatility.
- Market Hours: Currency markets operate 24 hours a day during the business week, and varying levels of activity and volatility occur depending on the time of day, with the most active periods usually coinciding with the overlap of the London, New York, and Asian trading sessions.
Trading tips for navigating Volatility in forex trading
Here are 10 important trading tips for navigating the forex market volatility.
- Risk Management: Prioritize risk management by setting clear stop-loss orders and never risking more than you can afford to lose.
- Use Leverage Wisely: If you use leverage, you may do so cautiously and be aware of its potential to amplify both potential gains and losses.
- Stay Informed: Keep track of economic calendars and major news events that can trigger market volatility and stay updated with market news.
- Technical Analysis: You may consider utilising technical analysis tools to indicate potential entry and exit points based on historical price patterns and indicators.
- Fundamental Analysis: Understand the underlying economic factors which may affect currencies, especially during key events like central bank decisions or economic data releases.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: You may consider avoiding putting all your capital into a single currency pair; instead you may diversify to spread risk.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: You may evaluate trades based on their risk-reward ratio
- Stay Disciplined: You may adhere to your trading plan and avoid emotional decisions or overtrading during volatile periods.
- Avoid Low Liquidity Times: Refrain from trading during periods of low liquidity, such as market closes and major holidays, to minimize erratic price movements.
Continuous Learning: Keep learning and adapting to changing market conditions and trading strategies to improve your strategy as a forex trader.
What volatility indicators to use?
A good sailor knows how to read the weather. Similarly, traders can use volatility indicators to indicate market movements. Here are some volatility indicators you may consider using:
- Average True Range (ATR): ATR can measure the average range between the high and low prices over a specified period. It may provide a quantitative measure of market volatility, potentially helping traders set stop-loss and take-profit levels.
- Bollinger Bands: Bollinger Bands consist of a middle moving average line and two outer bands that represent standard deviations from the average. Wider bands indicate higher volatility, while narrower bands may suggest lower volatility.
- Volatility Channels: Similar to Bollinger Bands, volatility channels use moving averages to create channels around price data. Breakouts from these channels can indicate potential increased volatility.
- Chaikin Volatility: This indicator can calculate the difference between the high and low prices over a specific period. It can help traders indicate potential trend changes and increased volatility.
- Average Directional Index (ADX): While primarily used for trend strength, ADX can also indicate the strength of potential price movements, which can be correlated with volatility.
- Relative Volatility Index (RVI): RVI can compare the closing price to the high-low range. It may help traders indicate overbought and oversold conditions and potential reversals.
- Historical Volatility: This indicator can measure past price movements over a given period, providing insight into how volatile an asset has been in the past.
- Implied Volatility (Options): Implied volatility is derived from options prices and may indicate market expectations of future volatility.
- Volatility Ratio: This ratio can divide the current day’s trading range by the average trading range over a specified period. Values above 1 indicate potential increased volatility.
- Volatility Index (VIX): While primarily associated with the stock market, the VIX can also be used as a gauge of overall market sentiment and potential volatility spikes in various markets, including forex.
- Donchian Channels: Donchian Channels may highlight the highest high and lowest low prices over a specified period. Breakouts from these channels can indicate shifts in volatility.
- Market News and Events: Besides technical indicators, staying informed about economic news releases, geopolitical events, and central bank decisions can help gauge and indicate market volatility.
The choice of volatility indicator depends on your trading strategy and preferences.
Key Takeaways:
- Volatility in forex trading refers to the degree of price variation in a trading price series over time, indicating the risk and uncertainty of returns.
- Volatility in forex trading is essential as it can offer both potential opportunities and risks. High volatility may indicate trading potential, while low volatility may indicate a more stable environment with fewer opportunities.
- Some of the most volatile currency pairs in the forex market include GBP/JPY, EUR/NZD, and AUD/JPY, known for significant price fluctuations.
- Traders may consider using various volatility indicators like Average True Range (ATR), Bollinger Bands, and Chaikin Volatility to assist them with assessment and navigation of market volatility.
- Volatility trading strategies may include the straddle strategy, delta hedging, and long volatility, each aligned to different market conditions.
- Market volatility in currency pairs may be affected by factors such as economic data releases, central bank decisions, geopolitical events, market sentiment, speculation, liquidity gaps, technical factors, external shocks, interest rates, trade relationships, and market hours.
- Effective risk management, disciplined trading, and continuous learning are essential elements for the construction of a dynamic trading strategy in volatile markets.
Conclusion:
Combination of skills, strategies, and a deep understanding of market dynamics are important key elements in order to navigate the unpredictable waves of market volatility in forex trading. Traders may need to adapt to changing conditions, employ volatility indicators, and use appropriate trading strategies to manage risks and seize potential opportunities. By staying informed, practising discipline, and choosing the right tools, traders can ride the volatility waves and make informed decisions in this dynamic and ever-changing market. However, keep in mind that high volatility in forex trading usually involves higher risks, therefore considering your risk tolerance and constructing a dynamic risk management plan can play an important role.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is provided for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended to be, nor does it constitute financial, investment or trading advice. You should not make any financial, investment or trading decision based on the information provided in this article without performing your own research or seeking advice from an independent advisor.



