
Participants in the Forex Market
Step into the heart of finance’s global arena – the forex market. A dynamic world where currencies sway to economic rhythms and geopolitical beats. In this thrilling realm, Central Banks, commercial giants, hedge funds, and retail traders converge. They dance with the ever-shifting values of currencies, managing risk, and shaping economies. Whether it’s the central bank steering policy, corporations hedging their earnings, or individuals trading online, each participant is important in this ever-changing financial system.
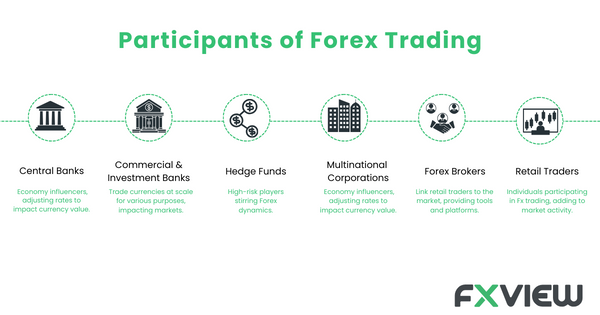
Who moves Participants in the Forex Market?
The forex (foreign exchange) market is a vast and decentralized financial marketplace where currencies are traded. It involves a wide range of participants, each with their own motives and objectives. Among the most influential participants in the forex market are:
1. Commercial Banks: Commercial banks are major players and critical participants in the forex market. They provide currency exchange services to clients, including businesses and individuals, and engage in forex trading to manage their own assets and liabilities.
2. Central Banks: Central banks participate in the forex market to implement monetary policy, exerting major influence as participants in the forex market. They may conduct foreign exchange operations to influence their domestic currency’s value and maintain exchange rate stability.
3. Investment Banks: As active participants in the forex market, investment banks engage in speculative trading. They aim to profit from currency price movements and often engage in large-scale transactions.
4. Multinational Corporations: These corporations are key participants in the forex market, entering to hedge against currency risk. They may use various strategies to protect their international business profits when dealing with multiple currencies.
5. Hedge Funds: Hedge funds, notable participants in the forex market, engage in speculative trading activities. They trade currencies to potentially capitalize on short-term price fluctuations, employing a wide range of strategies.
6. Retail Traders: Retail traders have become significant participants in the forex market through online trading platforms and retail forex brokers. They speculate on currency price movements, with the potential to make profits. Retail traders often use leverage to amplify their positions.
7. Market Makers: Market makers are essential participants in the forex market, providing liquidity by quoting bid and ask prices and facilitating traders in buying and selling currencies. Their role is crucial in maintaining market liquidity.
8. Speculators: Speculators, both individual and institutional, are active participants in the forex market. They trade to capitalize on currency price movements without the need for underlying transactions, adding liquidity and volume to the market.
9. Government Institutions: As participants in the forex market, some governments and their agencies directly engage to manage foreign exchange reserves, stabilize their currency’s value, or address trade imbalances.
10. Forex Brokers: Forex brokers act as intermediaries for other participants in the forex market, connecting retail traders with the broader interbank environment.
11. Payment Service Providers: These providers facilitate transactions for other participants in the forex market, aiding in cross-border trade and currency conversions for businesses and individuals.
12. International Corporations: Large international corporations are among the participants in the forex market, dealing with import and export business and managing currency exposure to protect against exchange rate movements.
13. Arbitrageurs: Arbitrageurs are savvy participants in the forex market, exploiting price discrepancies across different markets to earn profits.
14. Algorithmic Traders: Algorithmic traders, important participants in the forex market, use computer programs to conduct high-frequency trades based on market conditions.
15. ECN Brokers: ECN brokers serve as intermediaries between retail traders and the interbank forex market, another important conduit for participants in the forex market.
Understanding the roles of different participants in the forex market is essential for comprehending its complexity and the factors that influence currency prices. Each participant contributes to the market’s liquidity, volatility, and overall dynamics.
Key Takeaways
- The forex market is a vast and decentralized financial marketplace where currencies are traded.
- Key participants in the forex market include commercial banks, Central Banks, investment banks, multinational corporations, hedge funds, retail traders, market makers, speculators, government institutions, forex brokers, payment service providers, international corporations, arbitrageurs, and algorithmic traders.
- Each participant in the forex market has unique motives and objectives, contributing to market liquidity and volatility.
- Central banks and governments, as participants in the forex market, can have a significant impact on currency markets through interventions and policies.
Conclusion
The Forex market is not just a marketplace; it’s a reflection of the global economic landscape. It embodies the pulse of nations, the decisions of policymakers, and the strategies of traders, all coming together in a continuous symphony of buying and selling. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting to explore the world of forex, recognizing the roles and motivations of its diverse participants is fundamental to success. It’s a realm where knowledge, adaptability, and a deep understanding of the forces at play can unlock opportunities in a financial arena that never sleeps, where the potential for profit and the excitement of the chase is ever-present.
Disclaimer: The information contained in this article is provided for educational and informational purposes only and it is not intended to be, nor does it constitute financial, investment, or trading advice. You should not make any financial, investment, or trading decisions based on the information provided in this article without performing your own research or seeking advice from an independent advisor.



