
5 Key Factors Shaping Trading in Crude Oil: Geopolitical Risks and the Chinese Economy
The market in crude oil is dynamic and volatile, influenced by a variety of global factors. From geopolitical tensions to China’s economic downturn, oil prices and market trends shift dramatically. In this blog, we will explore 5 key factors shaping trading in crude oil with a focus on the Chinese economy & geopolitical risks and how they play a vital role in market fluctuations.
Impact of the Chinese Economy on Trading in Crude Oil
The Chinese economy is one of the world’s largest drivers of oil demand. As the world’s largest importer of crude oil, China’s economic health is proportional to international oil prices. When the Chinese economy slows down, demand for oil decreases, and this could lead to lower oil prices. However, when China’s economy grows, oil demand increases, surging up prices.
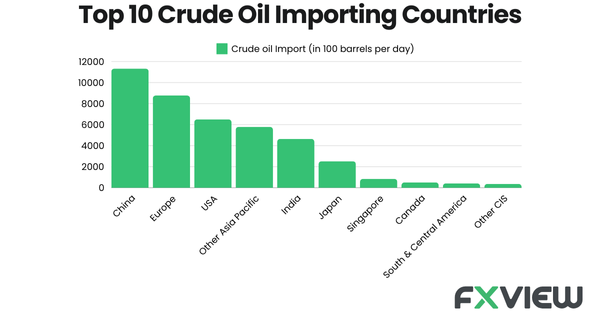
Recent signs of China’s growth have been a key concern for those involved in trading in crude oil. Despite efforts by Chinese authorities to stimulate the economy through fiscal and monetary policies, the country faces challenges like a slowing manufacturing sector and reduced industrial activity. These issues have led to a drop in China’s oil imports which fell by 9% in October, the sixth consecutive month showing a year-on-year dip on the other U.S. increasing its oil inventories, contributing to weaker demand for crude oil globally.
Furthermore, the crude oil market has also been impacted by China’s shift toward greener energy sources, such as electric vehicles (EVs). Since more cars in China are running on electricity, there is less of a need for petrol and diesel, which lowers the demand for oil overall. In the upcoming years, it is anticipated that this change and the nation’s initiatives to lower carbon emissions would continue to affect oil prices.
Geopolitical Risks
Geopolitical risks are one of the significant factors in trading in crude oil. Oil markets can be shaken by events like wars, diplomatic tensions, and political instability in oil-producing regions. Because traders expect shortages or delays in oil supplies, a disruption in supply from major oil-producing countries might cause shifts in the oil prices.
For instance, tensions in the Middle East often have a significant impact on oil prices. Conflicts involving countries like Iran, Saudi Arabia, or Iraq can cause disruptions to oil supply chains, leading to volatility in the market. Recent instability in Libya and Venezuela has raised concerns about potential supply shortages, which in turn has affected crude oil trading.
Additionally, geopolitical risks such as trade wars or sanctions can influence oil prices. The ongoing trade tensions between the U.S. and China have created uncertainty in global markets, including the oil sector. Rising tensions between major powers can also lead to market instability, as traders adjust their expectations about future oil supply and demand.
Furthermore, ongoing tension between Israel and Iran contributes to market volatility, as Iran continues exporting oil to major importers like China despite U.S. sanctions on both nations, impacting global oil prices. Also, the new Trump administration is anticipated to impose stronger sanctions on Iran and Venezuela, thereby reducing the world market’s supply of oil.
Other Factors Affecting Trading in Crude Oil
Apart from the Chinese economy and geopolitical factors, several other events impact trading in crude oil. These include:
OPEC+ Decisions: The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies, such as Russia, play a vital role in determining the world’s oil supply. When OPEC+ makes decisions to cut or increase production, it proportionally affects oil prices. For example, production cuts to balance global supply and demand often lead to higher prices, while production increases can push prices down. Also, OPEC+ has halted the new production till December 2024.
Global Economic Data: Oil prices may also be impacted by economic factors including growth rates & inflation data. Higher oil demand is usually the result of robust economic growth. On the other hand, poor economic data have the opposite impact. Also, by affecting the strength of the US dollar, which is used to price oil, central bank policies like interest rate hikes or cuts could affect oil prices.
Weather-Related Disruptions: Natural disasters like hurricanes or storms can disrupt oil production and transportation, particularly in the Gulf of Mexico, where a significant portion of U.S. oil production takes place for example recently hit Hurricane Rafael, which has caused 391,214 barrels per day of U.S. crude oil production to be shut. These disruptions cause short-term price fluctuations, as traders react to the potential supply constraints caused by weather events.
Oil Inventories: Trading in crude oil could be immediately affected by regular data on oil inventories, particularly from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Increases in oil inventories typically indicate excess or declining demand, which can drive down prices. On the other hand, a decrease in inventory might result in higher prices as it indicates a tightening market.
Key Takeaways
Here are the key points to remember regarding the factors while trading in crude oil:
- Geopolitical risks, such as tensions in the Middle East or sanctions on oil-producing countries, can cause significant price volatility in the oil market.
- The Chinese economy is a critical driver of global oil demand, and any signs of slowdown in China can negatively affect crude oil prices.
- OPEC+ production decision is a crucial factor that influences global oil supply and demand.
- Weather-related events, such as hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico, can cause temporary supply constraints, leading to short-term price fluctuations.
- Global economic data, including growth rates and central bank policies, could impact trading in crude oil by influencing demand and currency movements.
- Oil inventories, especially those in the U.S., play a significant role in shaping market expectations about supply and demand.
Conclusion
Many interconnected factors influence the environment of trading in crude oil. From the geopolitical risks that can disrupt supply to the Chinese economy’s impact on global demand, traders must constantly monitor these factors to make informed decisions. While short-term volatility is common, understanding the factors such as economic data, production levels, and geopolitical risks can provide valuable insights for the complex world of crude oil trading.
By staying informed about these key factors, we can better anticipate market movements and capitalise on opportunities in the evolving oil market.
Disclaimer: The information contained in this article is provided for educational and informational purposes only and it is not intended to be, nor does it constitute financial, investment, or trading advice. You should not make any financial, investment or trading decisions based on the information provided in this article without performing your own research or seeking advice from an independent advisor.




